XML and Excel are both extensively used for storing and exchanging data, but are very different in structure. XML is text structured in the form of a tree and Excel is proprietary data structured in the form of one or more tables. However you can easily convert XML to Excel format with Easy Data Transform:
- Download and install Easy Data Transform on your PC or Mac, if you haven’t done so already. It will only take a minute. There is a fully functional free trial and you don’t have to give us your email or sign up to anything.
- Start Easy Data Transform. Make sure the Auto Run button is pressed in.
- Drag the XML file you wish to convert onto Easy Data Transform. The file will typically have the extension .xml. A pink input item will be added.
- Notice in the Right pane that the XML data has has been ‘flattened’ into a table, suitable for output to an Excel .xlsx/.xls file. The nodes below the XML ‘root’ node are mapped to rows in Easy Data Transform.
- You can set the Format drop-down in the Right pane to Long or Wide, depending on whether you want the tables to have more rows or more columns.
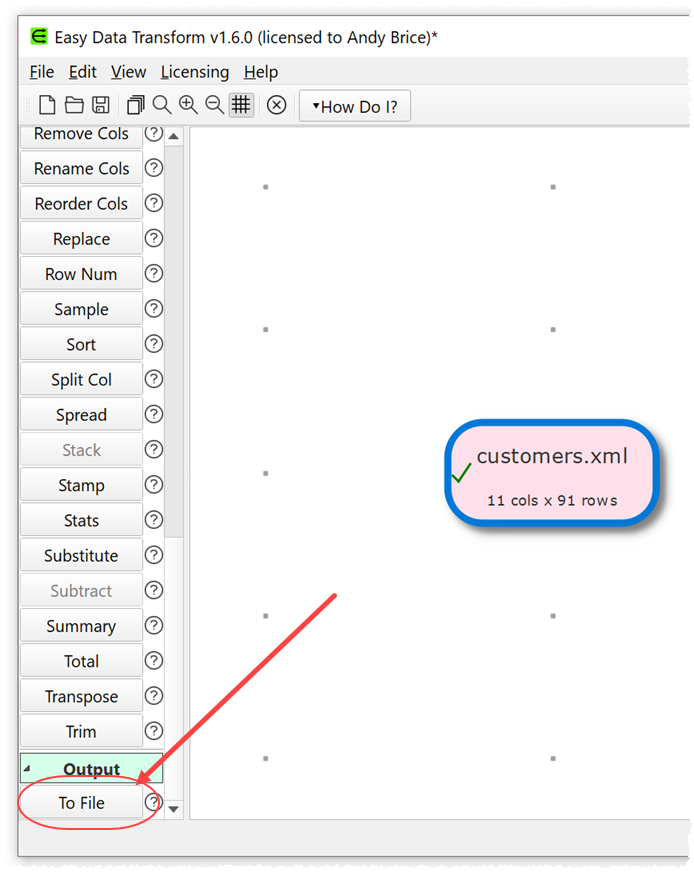
- Ensuring the pink input item is selected, click the To File button in the Left pane (scroll to the bottom of the Left pane).
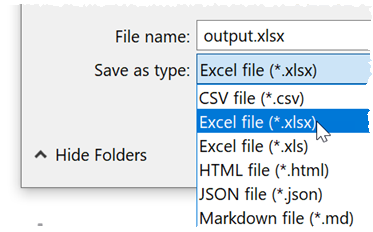
- A window will appear. Set the new file name and location. Select Excel file (*.xlsx) or Excel file (*.xls) as the file type.
- A green output item is added and selected.
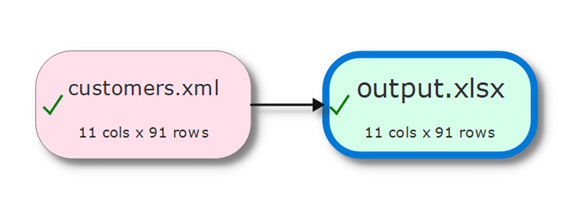
- The Excel file is created immediately at the chosen location, no need to ‘run’ anything.
Example XML input:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<root>
<record>
<CategoryID>1</CategoryID>
<CategoryName>Beverages</CategoryName>
<In_stock>true</In_stock>
</record>
<record>
<CategoryID>2</CategoryID>
<CategoryName>Condiments</CategoryName>
<In_stock>false</In_stock>
</record>
<record>
<CategoryID>3</CategoryID>
<CategoryName>Confections</CategoryName>
<In_stock>true</In_stock>
</record>
</root>
Example Excel output:
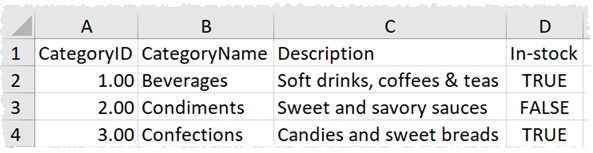
The dot (‘.’) character is used to show nesting of XML values and XML attribute values start with an underscore (‘_’). For example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<root>
<record carb="2" cholesterol="5" fiber="0"
name="Avocado Dip" protein="1" sodium="210">
<minerals>
<ca>0</ca>
<fe>0</fe>
</minerals>
<vitamins>
<a>0</a>
<c>0</c>
</vitamins>
</record>
</root>
Will be ‘flattened’ into Excel as:
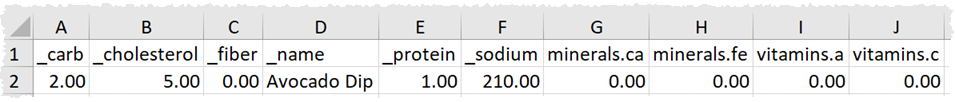
You can use a Rename Cols transform if you want to rename any of the columns before output.
If you have a large number of files to convert you can do it using batch processing.
You can do all this conversion offline. You do not need an Internet connection.
As well as changing file format, Easy Data Transform also allows you to combine 73 transforms (such as merge, dedupe and filter) to quickly and easily create simple or complex data transformations.
 Windows Download
Windows Download
 Mac Download
Mac Download